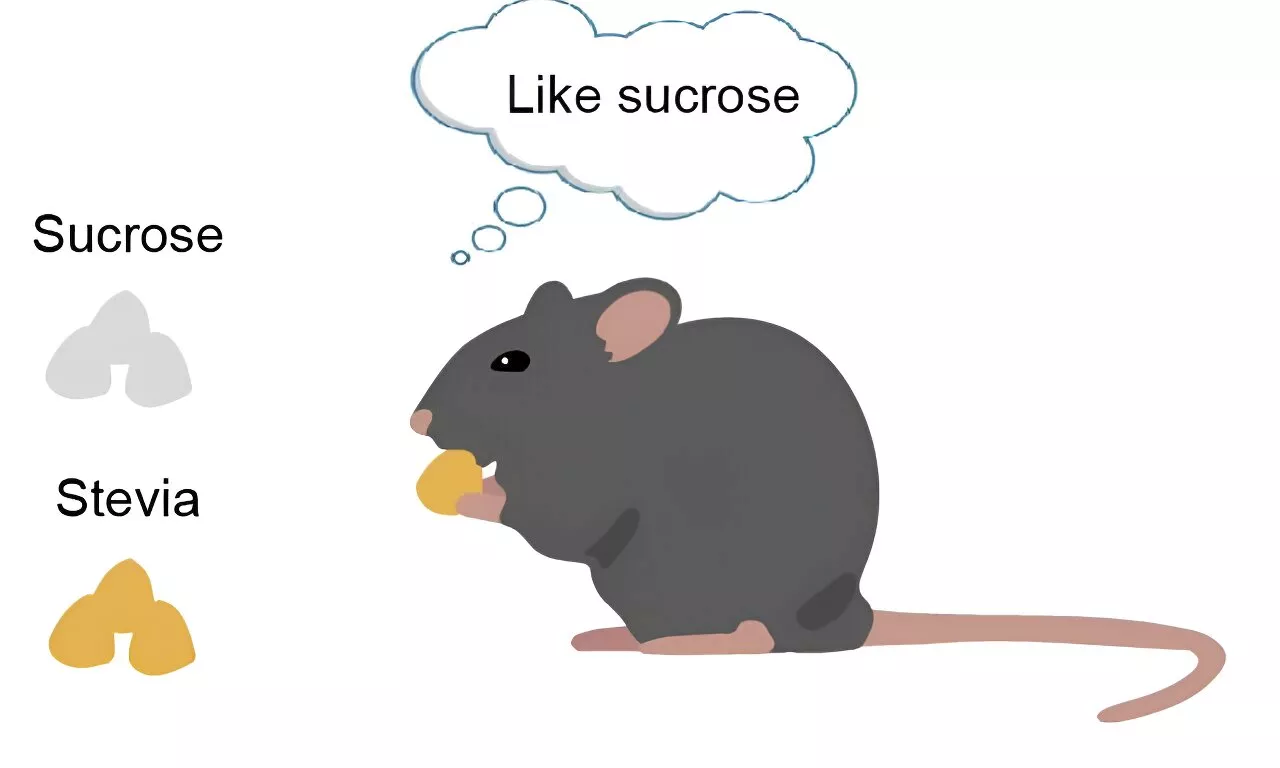
Given the known risks of consuming high amounts of sugar, today many people are looking for alternative sweeteners that produce a similar taste without prompting significant weight gain and causing other health issues.
Study suggests that stevia is the most brain-compatible sugar substitute retrieved 29 April 2024 from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2024-04-stevia-brain-compatible-sugar-substitute.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.Apr 26, 2024 Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use ourThank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Medical Xpress in any form.Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox.
Medicine Research Health Research News Health Research Health Science Medicine Science
Philippines Latest News, Philippines Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Sugar cravings could be caused by loneliness, study findsIf you've spent a lonely night at home eating chocolates and/or ice cream, you shouldn't feel guilty. That's because loneliness can cause an intense desire for sugary foods, a new study found.
Sugar cravings could be caused by loneliness, study findsIf you've spent a lonely night at home eating chocolates and/or ice cream, you shouldn't feel guilty. That's because loneliness can cause an intense desire for sugary foods, a new study found.
Read more »
 New study reveals key role vision plays in sculpting brain developmentScientists have long known that our brains are organized into specialized areas, each responsible for distinct tasks. The visual cortex processes what we see, for instance, while the motor cortex governs movement. But how these regions form—and how their neural building blocks differ—remain a mystery.
New study reveals key role vision plays in sculpting brain developmentScientists have long known that our brains are organized into specialized areas, each responsible for distinct tasks. The visual cortex processes what we see, for instance, while the motor cortex governs movement. But how these regions form—and how their neural building blocks differ—remain a mystery.
Read more »
 Brain dynamics and BMI linked to dieting success, study findsResearch reveals that individuals with higher BMI and extensive brain modifications during diet decisions tend to have lower success in diet modification, suggesting the impact of neural plasticity and BMI on diet adherence.
Brain dynamics and BMI linked to dieting success, study findsResearch reveals that individuals with higher BMI and extensive brain modifications during diet decisions tend to have lower success in diet modification, suggesting the impact of neural plasticity and BMI on diet adherence.
Read more »
 Stress activates brain regions linked to alcohol use disorder differently for women than men, finds studyWhen exposed to stress, people with alcohol use disorder engage parts of the brain associated with both stress and addiction, which may cause them to drink or crave alcohol after a stressful experience, suggest the authors of a study published in Alcohol: Clinical and Experimental Research.
Stress activates brain regions linked to alcohol use disorder differently for women than men, finds studyWhen exposed to stress, people with alcohol use disorder engage parts of the brain associated with both stress and addiction, which may cause them to drink or crave alcohol after a stressful experience, suggest the authors of a study published in Alcohol: Clinical and Experimental Research.
Read more »
 Study identifies potential strategy to diminish the devastating impacts of traumatic brain injuriesFor the roughly 1.5 million Americans per year who survive a traumatic brain injury, health outcomes vary widely.
Study identifies potential strategy to diminish the devastating impacts of traumatic brain injuriesFor the roughly 1.5 million Americans per year who survive a traumatic brain injury, health outcomes vary widely.
Read more »
