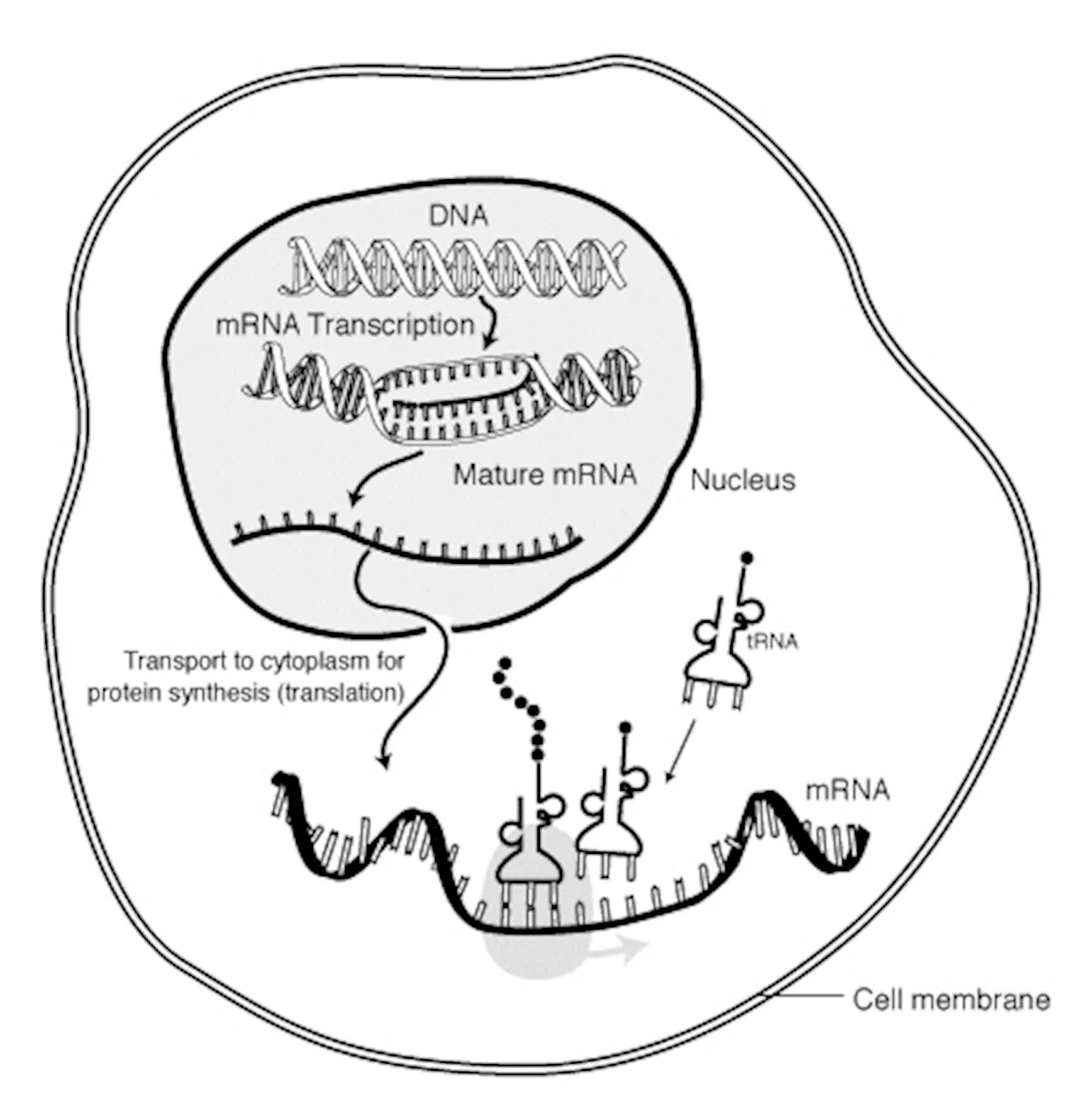
Messenger RNA (mRNA) made its big leap into the public limelight during the pandemic, thanks to its cornerstone role in several COVID-19 vaccines. But mRNAs, which are genetic sequences that instruct the body to produce proteins, are also being developed as a new class of drugs.
Messenger RNAs with multiple 'tails' could lead to more effective therapeutics, say researchers retrieved 22 March 2024 from https://phys.org/news/2024-03-messenger-rnas-multiple-tails-effective.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.Jun 8, 2022Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use ourThank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox.
Philippines Latest News, Philippines Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 mRNA vaccines may make unintended proteins, but there’s no evidence of harmAlterations that help messenger RNA persist in living cells can trip up protein synthesis
mRNA vaccines may make unintended proteins, but there’s no evidence of harmAlterations that help messenger RNA persist in living cells can trip up protein synthesis
Read more »
 Modeling the origins of life: New evidence for an 'RNA World'Scientists provide fresh insights on the origins of life, presenting compelling evidence supporting the 'RNA World' hypothesis. The study unveils an RNA enzyme that can make accurate copies of other functional RNA strands, while also allowing new variants of the molecule to emerge over time.
Modeling the origins of life: New evidence for an 'RNA World'Scientists provide fresh insights on the origins of life, presenting compelling evidence supporting the 'RNA World' hypothesis. The study unveils an RNA enzyme that can make accurate copies of other functional RNA strands, while also allowing new variants of the molecule to emerge over time.
Read more »
 RNA-based therapy shows promise against aggressive childhood brain tumors in miceTargeting a non-encoding stretch of RNA may help shrink tumors caused by an aggressive type of brain cancer in children, according to new research in mice.
RNA-based therapy shows promise against aggressive childhood brain tumors in miceTargeting a non-encoding stretch of RNA may help shrink tumors caused by an aggressive type of brain cancer in children, according to new research in mice.
Read more »
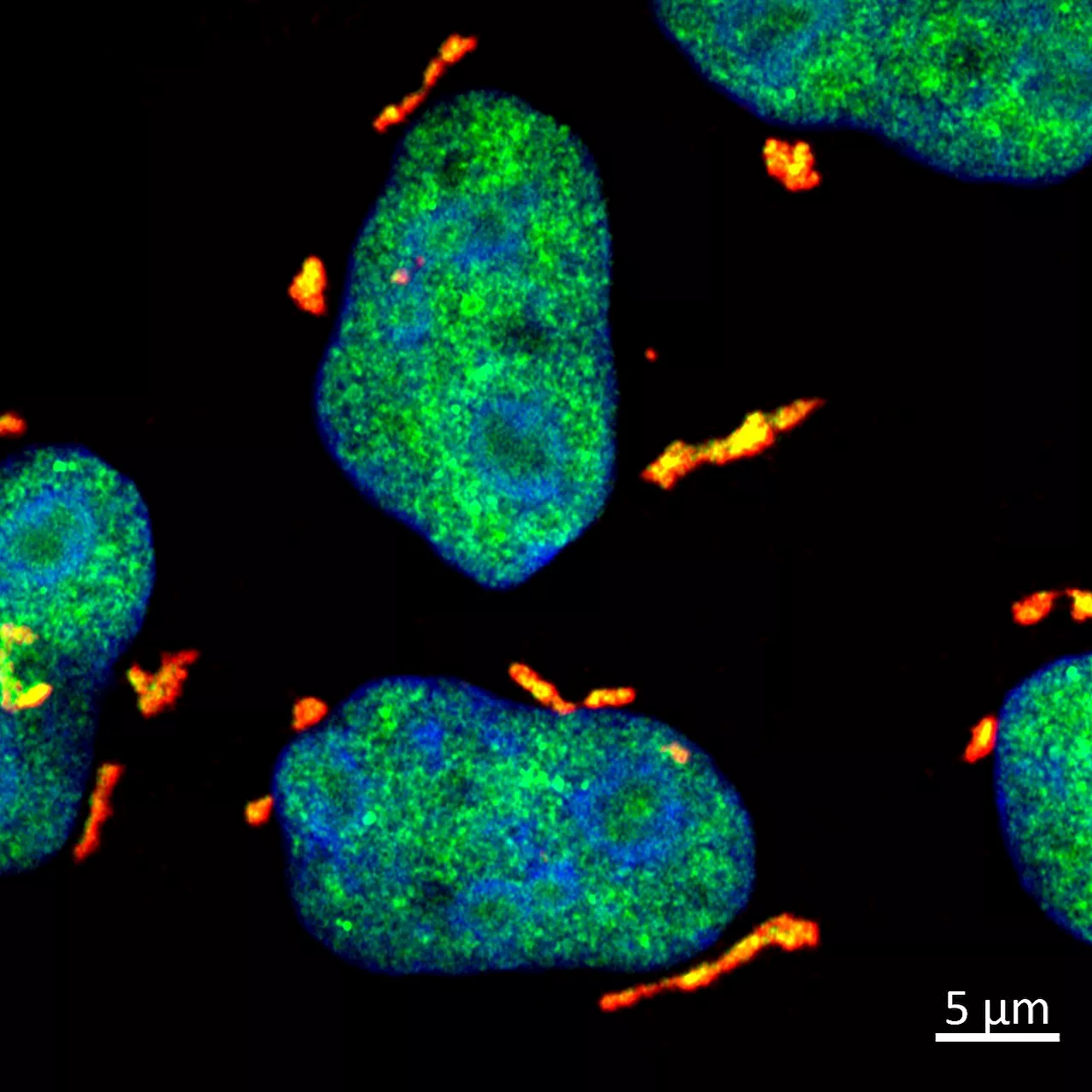 How DHX9 stress granules protect daughter cells from UV-induced RNA damageDuring the process of cell division, new daughter cells inherit a mix of genetic material and other molecules from their mother cells.
How DHX9 stress granules protect daughter cells from UV-induced RNA damageDuring the process of cell division, new daughter cells inherit a mix of genetic material and other molecules from their mother cells.
Read more »
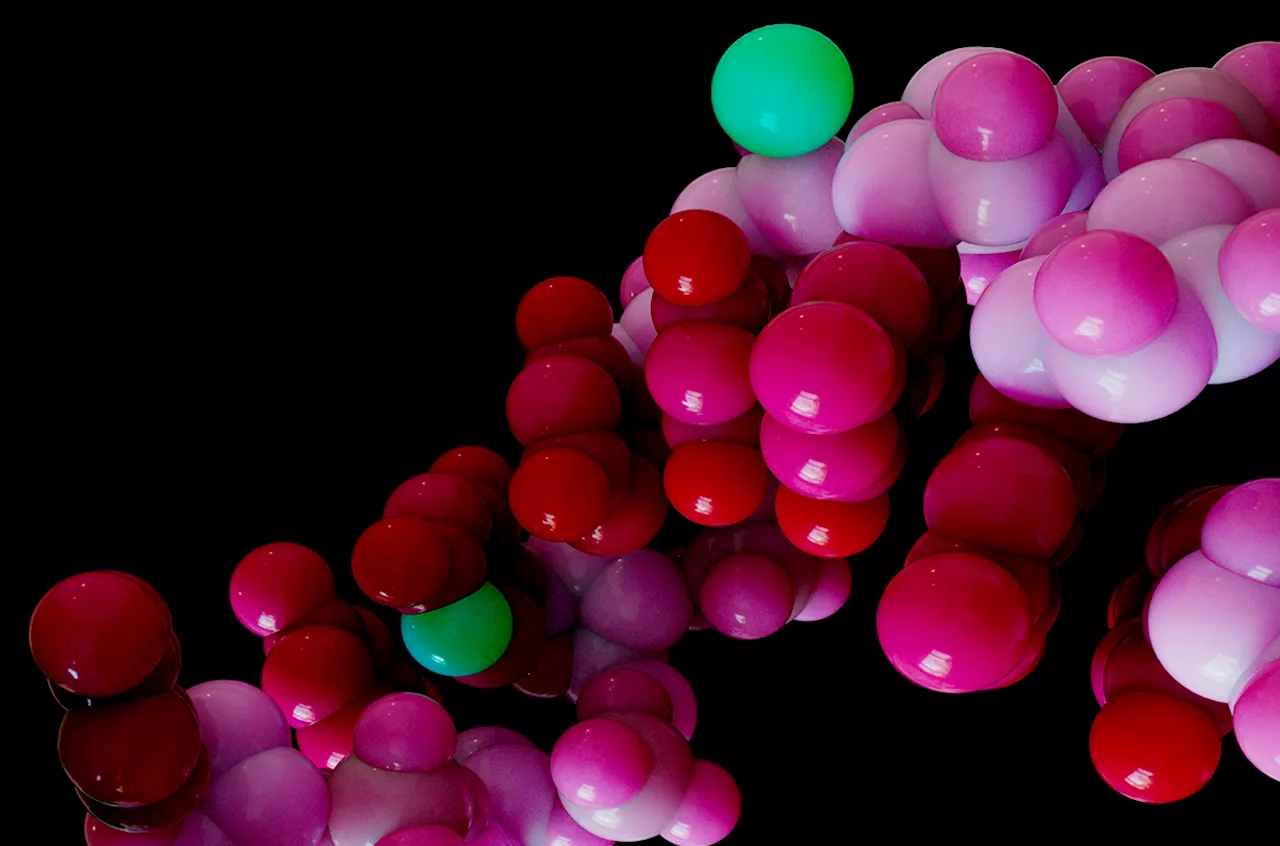 RNA deserves its own massive counterpart to the human genome project, researchers argueU.S. report lays out an ambitious plan to harness the “RNome” for medicine and more—but funding is uncertain
RNA deserves its own massive counterpart to the human genome project, researchers argueU.S. report lays out an ambitious plan to harness the “RNome” for medicine and more—but funding is uncertain
Read more »
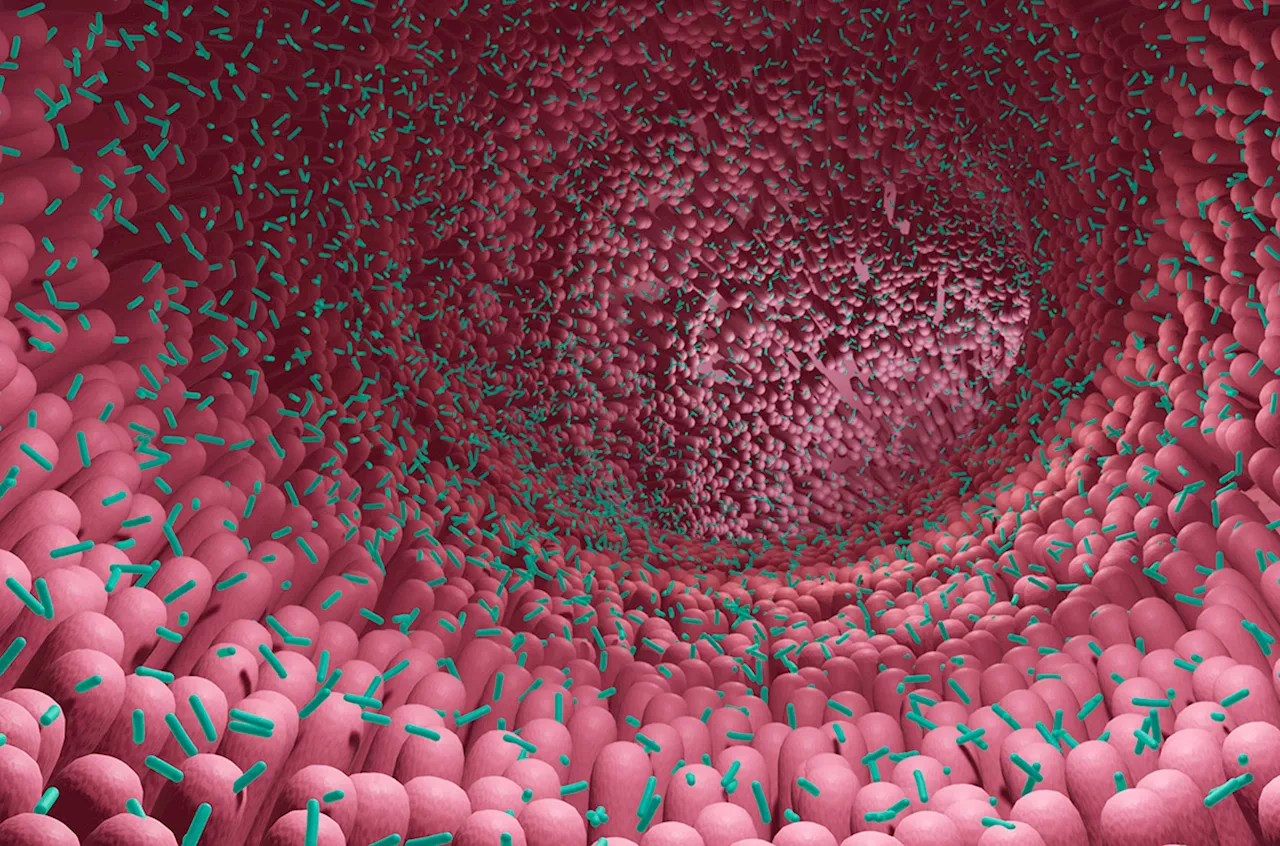 ‘It’s insane’: New viruslike entities found in human gut microbesAnalysis of sequence databases reveals novel circular RNA genomes belonging to “obelisks”
‘It’s insane’: New viruslike entities found in human gut microbesAnalysis of sequence databases reveals novel circular RNA genomes belonging to “obelisks”
Read more »